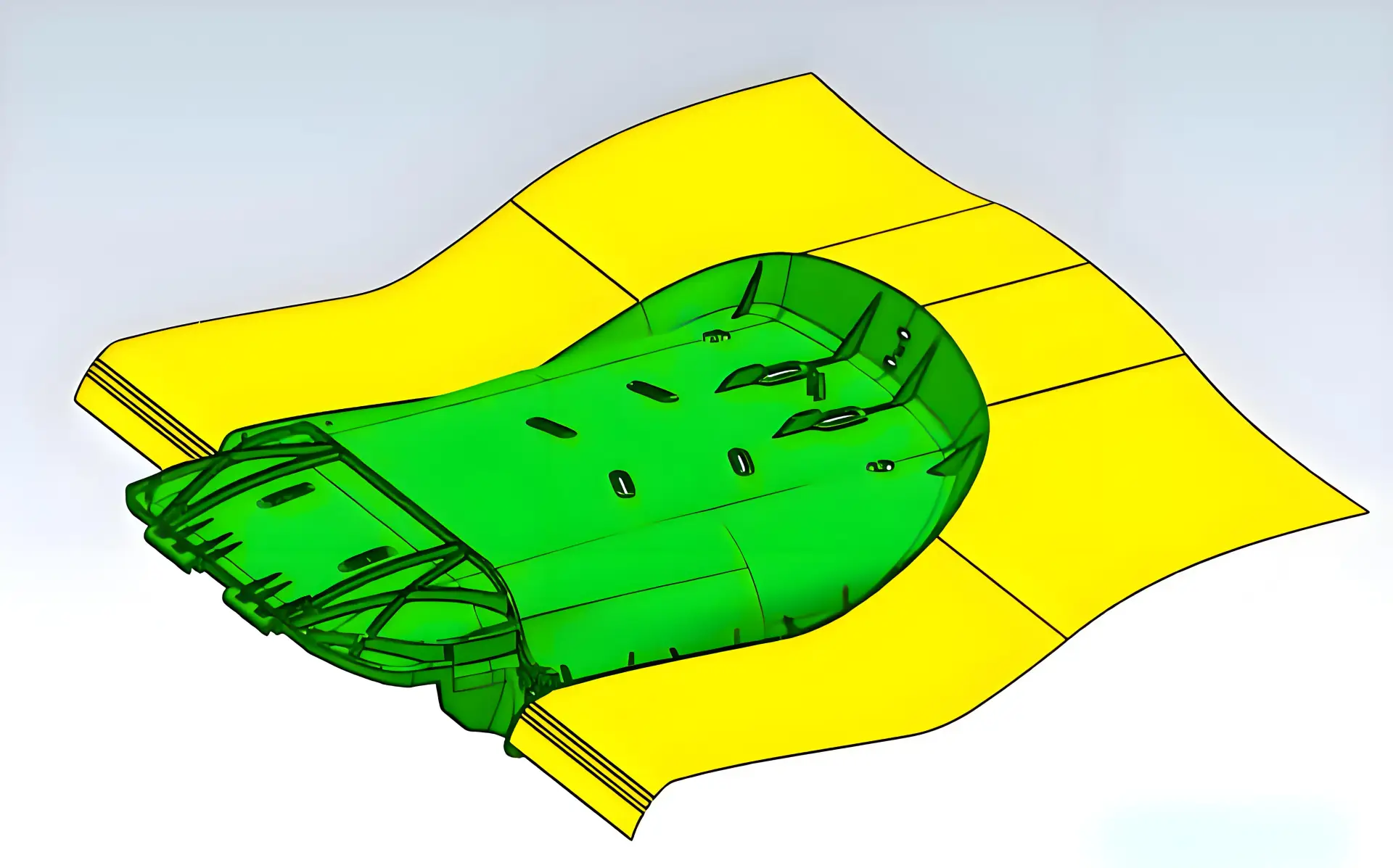
Basic Principles of Mechanical Design for Electronic Products
I. Introduction
The mechanical design of electronic products is a crucial part of the product design and development process, directly determining the product’s performance, reliability, lifespan, and user experience. This is fundamental to successfully Design a Product Shell. This article aims to elaborate on the basic principles of mechanical design for electronic products, including concise and efficient structures, reasonable material selection, flexible modular design, human-machine engineering optimization, uniform load distribution, stress concentration reduction, strength and stiffness enhancement, and the balance of aesthetics and practicality.
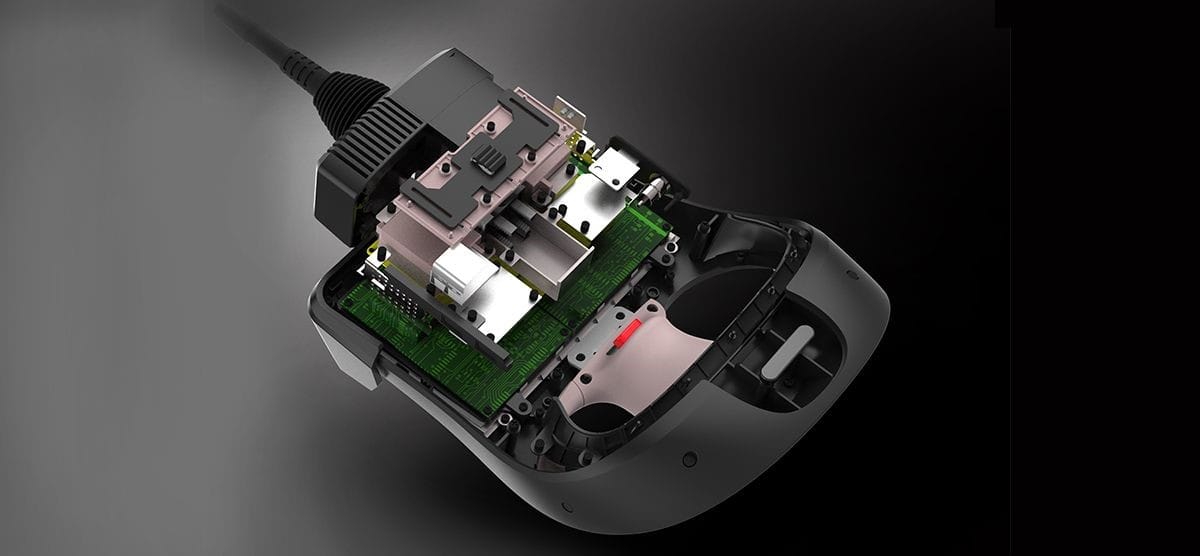
II. Basic Principles of Mechanical Design for Electronic Products
Concise and Efficient Structure
Concise and efficient structure is a fundamental requirement for the mechanical design of electronic products. In the design process, unnecessary components and complex assembly processes should be minimized to reduce manufacturing costs and improve production efficiency. At the same time, the product’s functional requirements should be fully considered to ensure that the structure is as simple as possible while satisfying the functional needs.
Reasonable Material Selection
Reasonable material selection has a significant impact on the performance and lifespan of the mechanical structure of electronic products. During the design phase, materials with excellent performance, reasonable costs, and ease of processing should be selected based on the product’s operating environment and functional requirements. Additionally, the environmental friendliness and sustainability of the materials should also be taken into account to meet the green development demands of modern society.
Flexible Modular Design
Flexible modular design enhances the flexibility and maintainability of the mechanical structure of electronic products. By dividing the product into multiple functional modules, it facilitates the expansion, upgrading, and maintenance of functions. Furthermore, modular design improves production efficiency and reduces production costs.
Human-Machine Engineering Optimization
Human-machine engineering optimization is the key to enhancing the user experience of electronic products. In the design process, the principles of ergonomics should be fully considered to ensure that the product’s operating interface, button layout, weight, and size comply with human physiological characteristics and usage habits. Additionally, the focus should be on the product’s safety, comfort, and ease of use to improve user satisfaction.
Uniform Load Distribution
In the mechanical design of electronic products, it is crucial to ensure uniform load distribution to avoid localized overloading. Through reasonable structural layout and connection methods, the loads borne by each component can be evenly distributed, improving the overall structural carrying capacity and stability.
Reduction of Stress Concentration
Reducing stress concentration helps enhance the fatigue life of the mechanical of electronic products. Design techniques such as rounding corners, using transitions, and implementing unloading measures should be adopted to reduce stress concentration in components under load, thereby minimizing the possibility of fatigue failure in Smart Rings.
Enhancement of Strength and Stiffness
Increasing the strength and stiffness of the mechanical structure of electronic products is essential to ensure stable and reliable product performance. In the design process, appropriate materials and structural forms should be selected, and reinforcement measures such as stiffeners and supports should be adopted to improve the overall structural strength and stiffness.
Balancing Aesthetics and Practicality
Balancing aesthetics and practicality is a dual objective in the mechanical design of electronic products. While pursuing aesthetics, the practicality and functionality of the product cannot be neglected. Designers should carefully consider the product’s appearance, color schemes, and details to create an attractive yet functional electronic product.
III. Conclusion
The mechanical design of electronic products is a comprehensive engineering task that requires adhering to a series of basic principles to ensure product performance, reliability, lifespan, and user experience. This article has provided a detailed elaboration on these principles, including concise and efficient structures, reasonable material selection, flexible modular design, human-machine engineering optimization, uniform load distribution, stress concentration reduction, strength and stiffness enhancement, and the balance of aesthetics and practicality. In practical design, designers should flexibly apply these principles based on the specific characteristics and requirements of the product to create electronic products with excellent performance and appealing aesthetics. This is essential for successful OPD design.